 |
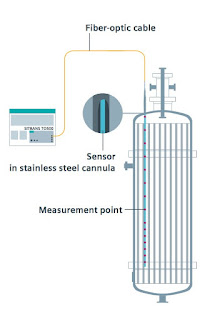
| Example of use (click for larger view) |
Recognizing temperature profiles and detailed understanding of the process are great challenges to plant operators. A fiber-optic based multipoint measuring system by SIEMENS enables you to determine a large number of temperature measuring points along a single sensor fiber and read out a temperature profile in a matter of seconds.
For example, you can quickly and precisely identify points overheating to help avoid or counteract potential damage to your product and/or equipment. Measured values are transmitted through an extremely thin sensor measuring lance. The diameter of the sensor measuring lance is independent of the number of measuring points. The response times of the sensors are also reduced because of the low thermal mass of the fiber optic.
Operation:
A continuously tunable laser generates light in the transmitter with a wavelength between 1500 and 1600 nm, which is output to the sensor measuring lances. The transmitter evaluates the reflected light component. Fiber Bragg Gratings (FBG) are inscribed at defined points on the sensor measuring lances, that reflect a defined wavelength. The wavelength reflected by the grating changes as a function of temperature and so indicates the temperature at the relevant measuring point. A gas cell with a fixed absorption line serves as a reference in the device, against which the determined wavelength is continuously calibrated.
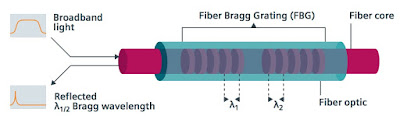 |
| Design of fiber measuring sensor (click for larger view) |
 |
| In use measuring catalytic conversion of gases in tube and tube-bundle reactors. |
- Tube and tube-bundle reactors
- Capillary and microreactors
- Distillation
- Rectifications
For more information in the SITRANS TO500 visit Ives Equipment or call (877) 768-1600.



